
B-Star is an easy-to-use
web server for high-resolution HLA star-allele typing from Oxford Nanopore (ONT) targeted whole-gene amplicon sequencing data.
B-Star is free and open to all users, with no login required, and the site does not use cookies (as shown on the landing page).
Designed to be easy for everyone
B-Star is built around a simple, guided workflow so you can go from raw reads to an interpretable report in just a few clicks.
What happens under the hood
B-Star provides end-to-end analysis for MHC class I HLA-A, HLA-B, and HLA-C, using curated reference sequences and the IPD-IMGT/HLA database for allele annotation.
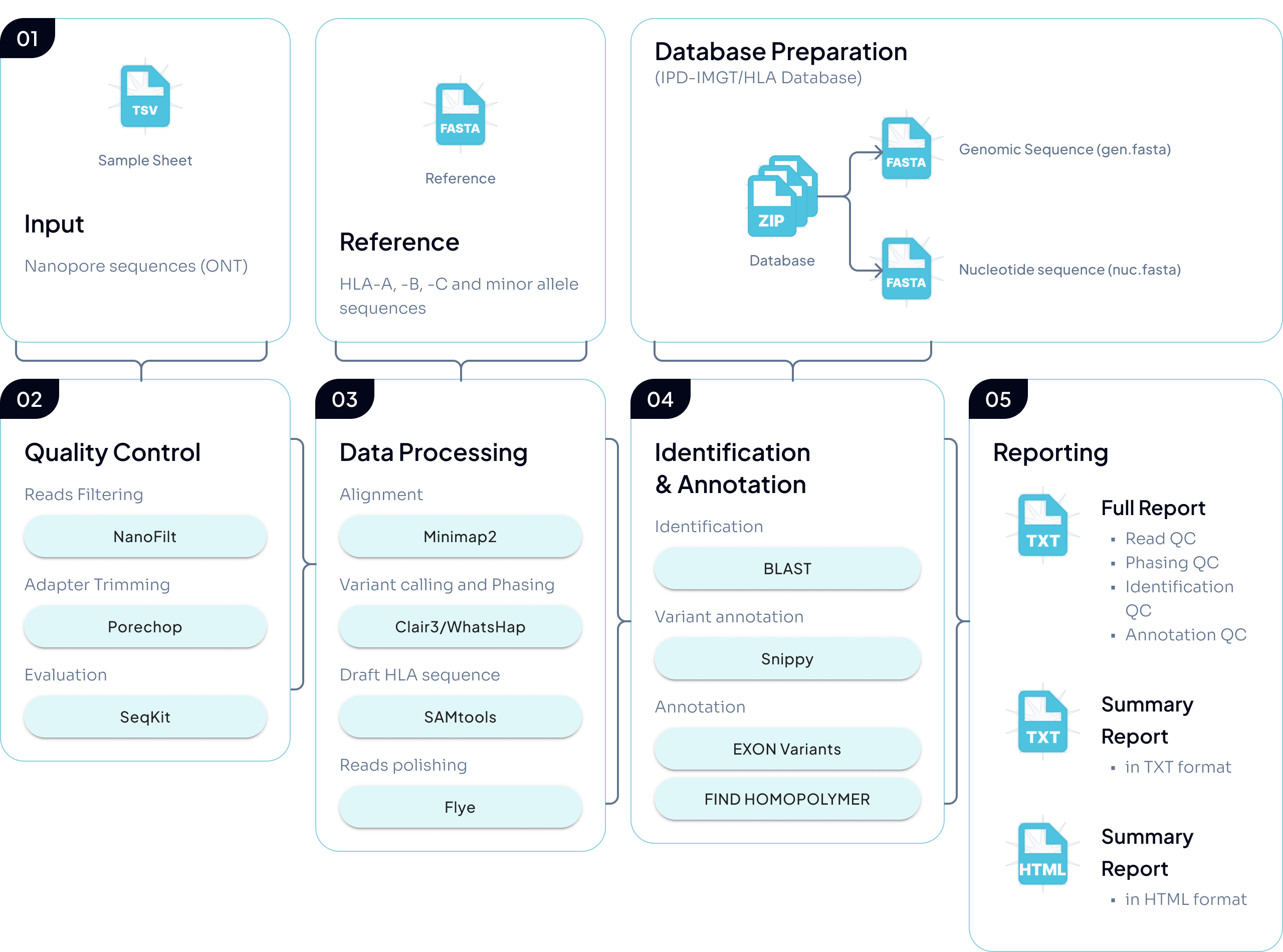
1. Inputs and reference preparation
B-Star takes ONT nanopore reads (in .fastq.gz or .fq.gz) as input and prepares an allele annotation reference based on IPD-IMGT/HLA.
2. Quality control
Reads undergo filtering/trimming and QC checks using standard tools (e.g., NanoFilt, Porechop, SeqKit).
3. Alignment, phasing, and consensus reconstruction
Reads are first aligned to HLA reference sequences and variants are called with Clair3. Heterozygous variants are then used for allele phasing with WhatsHap, which partitions reads by allele. Finally, each partition is used to reconstruct an allele-specific consensus sequence with Flye-polish (with supporting processing/formatting via tools such as SAMtools).
4. Allele identification and variant annotation
For each phased allele, the consensus sequence is searched against the IPD-IMGT/HLA reference database using BLAST to identify the best-matching reference allele. Differences between the consensus and the matched reference are then evaluated using Snippy.
• If there are no mismatches, or mismatches occur only in intronic regions, the allele annotation is reported as high quality.
• If a few mismatches are detected in exonic regions, the annotation is flagged (Inspect) and we recommend manual inspection of the allele assignment and supporting evidence.
5. Reporting
B-Star generates:
a full QC report in TXT formats
summary reports in TXT and HTML formats
Get Started!
Click "B-Star Pipeline" on the homepage,
upload your FASTQ file, and let
B-Star generate your HLA typing and report.
Notes and intended use
B-Star is designed to accelerate research and translational workflows by making high-resolution HLA typing and drug–allele risk annotation more accessible. The report is currently for research use only and has not been submitted for review to any regulatory agency. For any clinical decision-making, results should be interpreted within local policies and validated using appropriate clinical-grade procedures.